What is a Cataract?
A cataract is the gradual clouding of the natural lens inside the eye, leading to blurred vision, difficulty with daily tasks, and a decline in overall quality of life. The lens of the eye normally helps to focus light onto the retina for clear vision. Over time, proteins in the lens begin to break down and clump together, creating cloudy patches. This condition is called a cataract.
Most commonly, cataracts develop as a natural part of aging. However, factors such as diabetes, long-term use of certain medications, eye injuries, prolonged exposure to UV rays, or even hereditary traits can also lead to early cataract formation. Left untreated, cataracts can progress to advanced stages, causing significant vision loss and even blindness.
For cataract patients treatment is now safer, faster, and more comfortable than ever before, thanks to modern technology and expert cataract surgeons.
Types of Cataracts
Understanding the type of cataract you have is essential in determining the right treatment. At Vala Eye Centre, our cataract specialists in Vadodara carefully diagnose each case and recommend the best treatment plan.
Symptoms of Cataract
If you notice any of the below symptoms, it’s time to consult an ophthalmologist for a complete eye examination. Early detection can prevent unnecessary struggles in your day-to-day life.
- Blurry or cloudy vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Sensitivity to glare and bright lights
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Frequent changes in prescription glasses or contact lenses
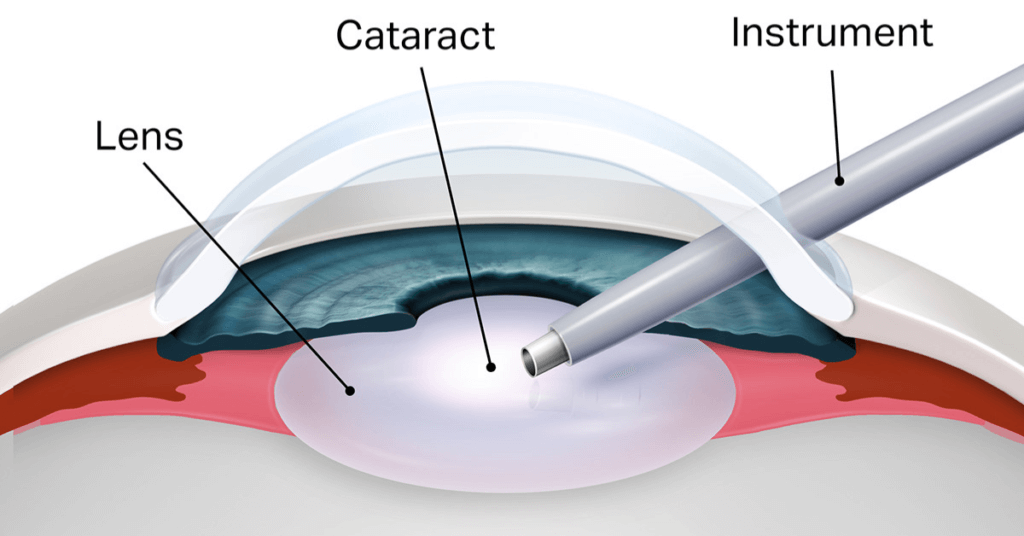
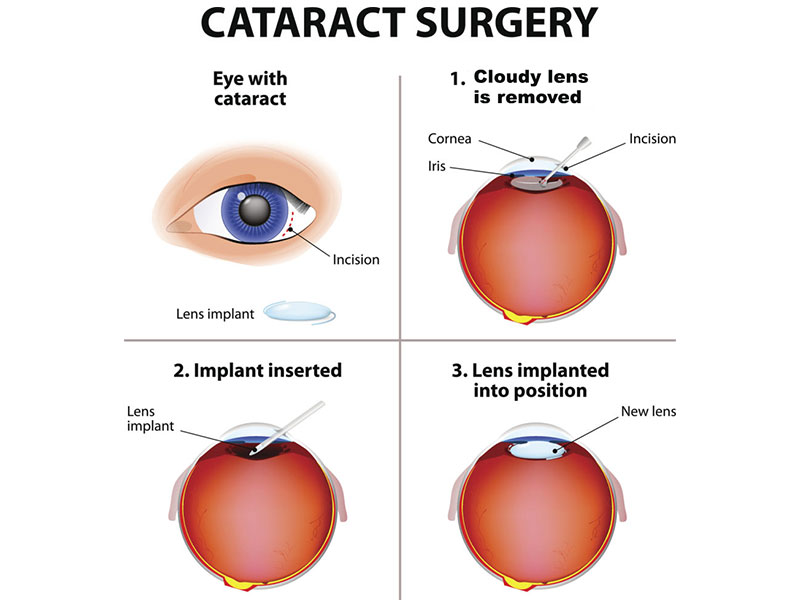

Advanced Cataract Surgery Techniques at Vala Eye Centre
- 1. Phacoemulsification (Phaco Surgery)
A small incision technique where the cataract is broken down using ultrasonic vibrations and replaced with a clear IOL. Benefits include:
- Stitch-less surgery
- Same-day discharge
- Minimal recovery time
- 2. Bladeless Laser Cataract Surgery
A highly advanced technique where a femtosecond laser performs precise steps of the surgery, offering: - Greater safety
- increased accuracy
- Enhanced Visual outcomes With both techniques available, our specialists at Vala Eye Centre provide the best treatment and comprehensive care to all the patients seeking eye treatment. Intraocular Lens (IOL) Options
- Monofocal Lenses: Clear distance vision; glasses needed for near tasks.
- Multifocal Lenses: Provide both near and distance vision; reduce dependence on glasses.<
- Toric Lenses: Correct astigmatism along with cataracts.
- Team of experienced cataract surgeons with years of experience provide best cataract surgery in Vadodara
- State-of-the-art technology for precise diagnosis and treatment
- Affordable cataract surgery packages in Vadodara
- Personalized consultation and lens options based on your needs
- Comfortable facilities with compassionate aftercare by our eye specialist
- Protective eye gear
- Eye drops and medications for healing
- Step-by-step recovery instructions for patient.
- Scheduled follow-up consultations
The choice of lens plays a major role in your vision after surgery. We offer a range of IOLs, including:
Our cataract specialists guide you through these options to ensure the lens chosen matches your lifestyle, whether it’s reading, driving, or working on digital devices. Why Choose Vala Eye Centre for Cataract Surgery in Vadodara?
Recovery & Aftercare of Cataract Surgery
One of the greatest advantages of modern cataract surgery is the fast recovery. Most patients notice a significant improvement in vision within 24–48 hours.
Our patients appreciate that their recovery journey is smooth, comfortable, and closely monitored by our specialists.
Click here to Read FAQs related to Cataract
Book a Consultation with Dr. Ruchi Vala – Cataract Specialist in Vadodara
If you or your loved ones are experiencing vision problems due to cataracts, don’t wait until it worsens. Schedule a consultation with our expert doctors today and take the first step towards clearer, brighter vision.
Book an appointment or Visit Vala Eye Centre, Vadodara – your trusted and best eye hospital in Vadodara for advanced cataract eye treatment.
